Smart Contracts on the Ethereum blockchain are essential to maintain the network’s transactions by keeping them decentralized and seamless. These automated programs are almost like AI as they don’t require human approval and help speed up the processes 100x times.
For someone who isn’t familiar with blockchain technology and its mechanics, smart contracts might seem a complex concept to grasp since it’s highly discussed in the DeFi, crypto, NFTs, metaverse, and Web3 space. This guide will help you fully understand what exactly are smart contracts, their utility, and how they work.
What is a Smart Contract?
Smart Contracts are automated programs that only process an operation or transaction once the pre-conditions written on them are met, similar to the if/then statements.
To explain it better, here’s an example: on the Ethereum blockchain, if the “step 1” condition is met, then “step 2” will be executed and recorded on the ledger instantly for the public to see.
These programs are kind of similar to how third-party works, so it removes their role from the exchange between two parties by automating the conditions, and this is what makes them decentralized.
For instance, when you send money to someone, the bank is the middle party in between. You need the bank’s approval or the bank will oversee the transaction before you transfer it, but with the smart contract, the monetary exchange is direct owner to consumer or vice versa.
These computer programs aren’t just singularly fed, instead, they are attached together as a string on any decentralized platform or application. These can also include non-fungible tokens, DAOs, dApps, DeFi protocols, etc.
Background
When Satoshi Nakamoto, the presumed creator of Bitcoin and cryptocurrency, presented his paper in 2008, he wanted to invent a system that removes the role of the third party or centralized authority and gives users ownership over their assets in digital form. However, there wasn’t any mention of a smart contract in the paper he published.
The history of smart contracts goes way further back in the 1990s presented by Nick Szabo, an American cryptographer, and computer scientist as a “set of promises,” who is widely known for inventing the virtual currency “Bit Gold” in 1998. But this concept didn’t come to life until the Ethereum blockchain introduced smart contracts in the 2010s.
Smart contracts have always existed but with centralized authority involved. The idea of using it in decentralization was different because it removes the role of third-party completely.
In fact, the ETH network is the pioneering blockchain for utilizing these computer programs for approving transactions. Since then, they have been massively experimented with by different protocols, dApps, NFTs, and blockchain networks to expand their utility.
Many people believe only professional programmers can use these programs but they’re wrong. Even if you don’t have a background in programming or computer science, you can still utilize it and apply it.
What are NFT smart contracts?
NFT smart contracts are one of the essential programs for any project because they ensure the trading, burning, staking, and distribution of rewards & royalties are seamless and decentralized.
Every non-fungible token has a smart contract attached that feeds the data and transactions on the ledger. Additionally, if a physical artwork is tokenized, the smart contract helps in keeping the ownership and data safe on the blockchain.
NFT smart contracts have a lot of utility for any project’s ecosystem. Since this industry is highly based on transparency, fair distribution, and creator royalty, these programs work as a peace treaty to regulate the community of any project. In other words, no third party can get involved and no one can assert their power in any way.
How to view NFT contracts?
You can also view any token’s smart contract details on the Ethereum blockchain. Users can easily list all the information about the NFT, its transfers, sellers, and any other tasks it went through on the network.
There are mainly two ways to view NFT contract real-time details: Etherscan or NFT marketplace.
Etherscan
This block explorer records all information related to the token’s smart contract. It’s similar to a browser, except instead of using keywords, you enter the wallet address, block number, token name, or ENS address.
Etherscan is a really big search bar that digs the whole blockchain to find the relevant information; therefore, it’s important to feed accurate details when searching for a token. For example, if you just search Bored Ape Yacht Club, then you will see thousands of results on it, only the one with a blue checkmark is a legitimate address among many.
But if you’re looking for a specific token, then you need to type a certain token address of the NFT, and you will see the exact information of it.
How to view token address on Etherscan
To view the NFT’s smart contract, simply follow the below steps:
- Go to etherscan.io
- Enter the NFT collection you’re looking for
- Click on the top result with a blue verification mark
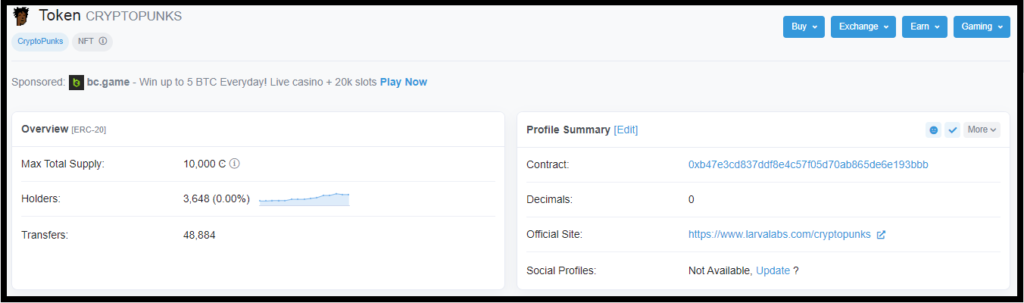
- Go to the right side, and select Profile Summary Card to ensure it’s verified
- Click on the link beside the Contract on the Profile Summary
- The page will direct you to the token’s smart contract
How to read on Etherscan
Etherscan can be quite complex for some people, especially those who are new to the space. Seeing the main page can easily confuse you as to what you should be looking at and whether it is relevant to your research or not. On Etherscan, you can see the transactions, contracts, code, analytics, and other operations already happened or are happening on the blockchain.
When you land on the website, you will first see a Search bar where you can look for specific tokens or addresses. Below, on the left side are the latest blocks that took place in real-time, while on the right side are the latest transactions on the blockchain.
All of the information is written via wallet addresses, so if you don’t know any company or project’s wallet address, it’s impossible to identify who they belong to, and this is how blockchain technology maintains the privacy on the ledger.
Moving towards navigating through Etherscan, let’s suppose you’re looking into a token’s contract. First, follow the above steps to land on the main contract page, here you will see the Overview and More Info.
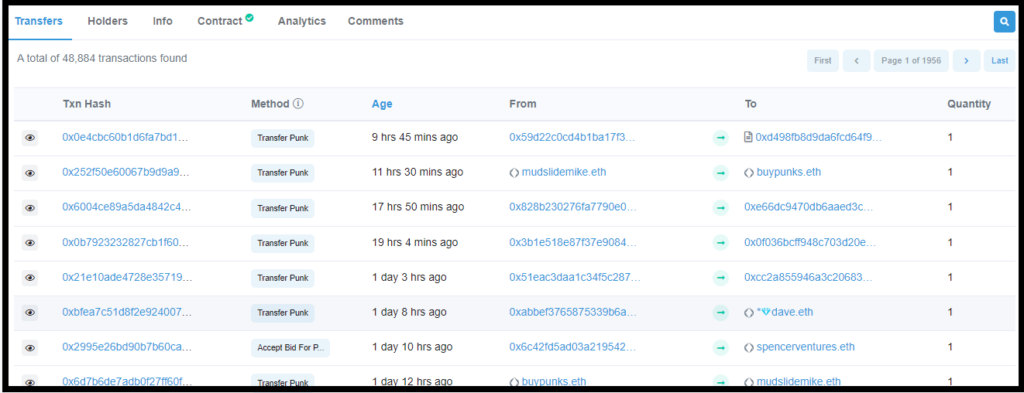
Scroll down, you will see a big table with tabs. Transfers show all the wallet addresses and transactions that took place within the NFT collection, Holders show all the names and addresses of owners, and Info & Contracts view all the details and the source code, security audit, and creation code of the token. The Analytics tab features a chart representation of transfers.
NFT Marketplace
Another way to access contracts is trading platforms or marketplaces that have all the NFT collections listed with all the information. It is much simpler and easier than searching on Etherscan.
Many marketplaces like OpenSea, Magic Eden, and Rarible show all the technical network details about the token. On OpenSea, simply click on a collectible, Click on the Contract address link, and you will be redirected to the token page.
On Rarible, the contract address can be accessed through the mint transaction option; it directs users to Etherscan where they can click on the link to see the token’s contract.
Utility of Smart Contracts
Now you know all about these computer programs but you might wonder what’s their utility. Well, smart contracts are predicted to become more and more complex as assets become tokenized because this automated software is vital to blockchain technology.
The following are the benefits of smart contracts:
- Security: No transaction is made until the precondition is made, the data is highly encrypted, making it hard for attackers to decrypt
- Scalability: the operations are smooth because they are automatic and quick
- Accuracy: the data fed on the ledger is precise without any bias
- Transparency: Anyone can view the transactions of tokens
- Save money: it removes the role of a third-party, so no extra charges are liable for both parties.
Final words
Smart contracts are the best invention up-to-date that play an essential role in the ideology of making the digital economy decentralized and safe. Although Web3 technology is still in its early stages, these automated programs are most likely to become more advanced as developers and creators realize their utility in real-world transactions.
Furthermore, since these programs help in establishing digital ownership over assets and personal information, they will influence the overall exchanges around the world. Every company, intelligence agency, or government will not be allowed to misuse people’s information for personal gain.
All in all, smart contracts offer authenticity, trust, anonymity, and credibility between two parties on the blockchain.