Blockchain is the new era of the internet that redefines our interaction with the world. By overcoming the limitations of dotcom and introducing the concept of ownership, this new technology is gaining a lot of attention publicly.
People often confuse blockchain with cryptocurrency, which are two completely different concepts. Blockchain is a decentralized network, while cryptocurrency is digital money that operates on it and where transactions happen between two parties. All of this is part of Web 3.0, the successor of Web2.
This technology is considered the safest and most authentic when storing sensitive information or interactions. Many companies and individuals have recognized this innovation and are actively adapting to it by introducing new initiatives within the Web3 space.
However, since every business model or transaction is built differently, it’s important to know what type you are adopting. This article is a guide to knowing blockchain and its types.
What is a blockchain?
Blockchain derives from two words “block” and “chain.” It’s basically a system that stores data in a block, once that block is full, a new block is created, which is attached together in the form of a chain. The data is shared and approved in a decentralized, peer-to-peer network, completely removing the central authority.
In other words, blockchain is a shared public ledger where all recorded transactions of digital assets, tangible or intangible, are displayed while maintaining the privacy of the users. Furthermore, the ownership of data belongs to the user, and they hold the power to share data with whoever they want to and how much they want to.
4 Types of Blockchain Networks with Examples
Blockchain is mainly of four types. Corporations decide between what network is perfect for them and whether it suits their goals.
1. Public blockchain
This type of blockchain allows anyone to join and validate transactions. It is fully decentralized because data is distributed equally to every peer or node in the network; they have the right to view transactions, access blockchain, produce new blocks, and approve blocks.
The adoption of a public blockchain is more common because anyone with the internet and good computer equipment can join. Furthermore, they can even earn something in return for their services in the form of native cryptocurrency.
Example:
Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana are use cases of this type. They are built on either the proof-of-work or proof-of-stake models, where nodes approve transactions. In Bitcoin mining, miners make transactions by solving cryptography to add new blocks, while in Ethereum staking, users who staked coins, chosen randomly, act as nodes and approve transactions.
Pros:
- Promote mass adoption
- Safe and Secure
- Democratized, every node gets a copy of the ledger
- Anonymity is maintained
Cons:
- Processing is slow
- Consumes high energy because of supercomputers
2. Private Blockchain
Most companies and businesses utilize the private blockchain to keep their sensitive data safe and secure from outsiders. This type is also known as a Managed blockchain because although it is decentralized to some extent, it’s quite small compared to the public one.
Only selected individuals are added to this network, while those without access cannot view the information shared inside. Additionally, some authorized users maintain control.
Example
Pros:
The use case of this type is Ethereum Enterprise. Although ETH is public, the Ethereum Enterprise is private because it is specially made for businesses to utilize private chains and even the public network. IBM, R3 Corda, Hyperledger, and Tezos also offer private blockchains.
- Scalability
- Only a few individuals can access
- High transaction speed
- Privacy
Cons:
- Low security
- Authorized transactions
- Fewer nodes = less activity
3. Hybrid Blockchain
A hybrid blockchain is controlled by a centralized authority but also decentralized to some extent. In other words, it’s a blend of both public and private models into one blockchain. The data is private, but certain transactions are approved public via a smart contract.
Example
The Ripple network (XRP) is a great example of a Hybrid model. The healthcare, real estate, retail, and supply chain sectors can also utilize this to maintain data anonymity yet still share the processes.
Pros:
- Safe from 51% attack
- Cheaper gas fee for the transactions
- Choose between what to make public and what to keep private
Cons:
- Fewer incentives for nodes
- Non-transparent with sharing data
- Inefficient maintenance
4. Consortium Blockchain
Also known as the federated blockchain, this type is controlled by many organizations instead of just one. It is much more decentralized yet secure than private blockchain because different members work together to run it smoothly. Some part of it is permissionless, while some is regulated by the authorities.
This type of blockchain is usually suitable for organizations that are working together for similar goals.
Example:
Tendermint and Multichain are big examples of consortium blockchains. This technology is suitable for Banks and other payment platforms that need to share information closely with one another while maintaining privacy.
Pros:
- Multiple authority
- Privacy and Transparency within the network
- High-speed transactions
Cons:
- Approval is needed from all members
- Might lead to corruption
- High vulnerability to a data breach
Types of blockchain in cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency is usually operated on public or private blockchains but some companies also utilize hybrid and consortium as well. It depends on what type of crypto token it is. Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana, and MATIC are also examples of public blockchains as they are more decentralized.
Usually, private blockchains don’t need a cryptocurrency because they are focused on within organizations or companies.
Blockchain technology in different industries
Blockchain technology has an infinite amount of utility that is yet to be explored by different entities around the world. So far, many industries are already experimenting with it, while some have already integrated them into their model.
Here is how blockchain can be utilized in different industries:
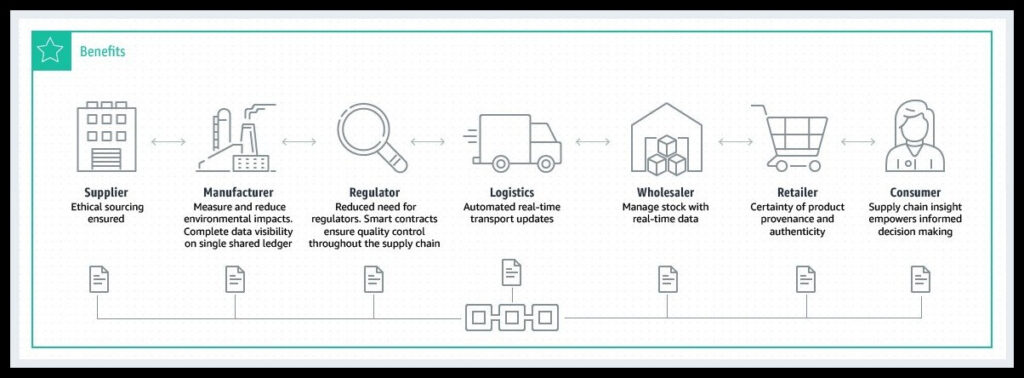
Supply Chain
Supply Chain Management is a challenging sector as it involves data privacy and interaction between organizations to deliver products on time. The private, hybrid, and consortium models are the most used cases in this sector.
Pharmaceutical
Blockchain technology in pharmaceuticals can be utilized for product distribution, prevention, tracking, and privacy. A lot of research studies are being done currently to deeply understand how this tech can overcome the existing limitations.
Many experts believe blockchain can remove the threats of malpractice because data is stored on a public ledger and everyone can view it to ensure they are in safe hands.
Healthcare
The Healthcare industry is in dire need of blockchain technology because it can solve so many problems surrounding patient data storage and privacy. For example, if an American patient on a trip to Maldives suddenly becomes ill, if their data is stored on a blockchain, the staff can easily access the patient’s medical history to give effective treatment.
Similarly, there are dozens of examples of how the healthcare sector can easily adopt this new technology in its favor. In fact, there are many blockchain companies already launched that are suitable for hospitals such as BurstIQ, MedicalChain, Guardtime, Coral Health, and many more.
Education
Education through blockchain technology can open up new doorways to practical experience and knowledge. The traditional curriculum is based on textbooks, with blockchain, students can learn in immersive computer-generated environments such as the Metaverse.
Furthermore, blockchain can connect parents, teachers, and students on one platform to interact closely and solve any gaps or problems. Parents would know what their child is taught, teachers will understand the student better, and the student can absorb concepts in a fun way.
Final words
Every type of blockchain has unique characteristics, making it preferable for one party but not for another. It is entirely impossible to pick one type that is best or worst. However, if we look at the most common, the public blockchain is widely adopted.
This article was a guide to knowing everything about blockchain, its types, and its strengths & weaknesses so that even if you aren’t a professional, you should still have background knowledge about what this technology actually is.