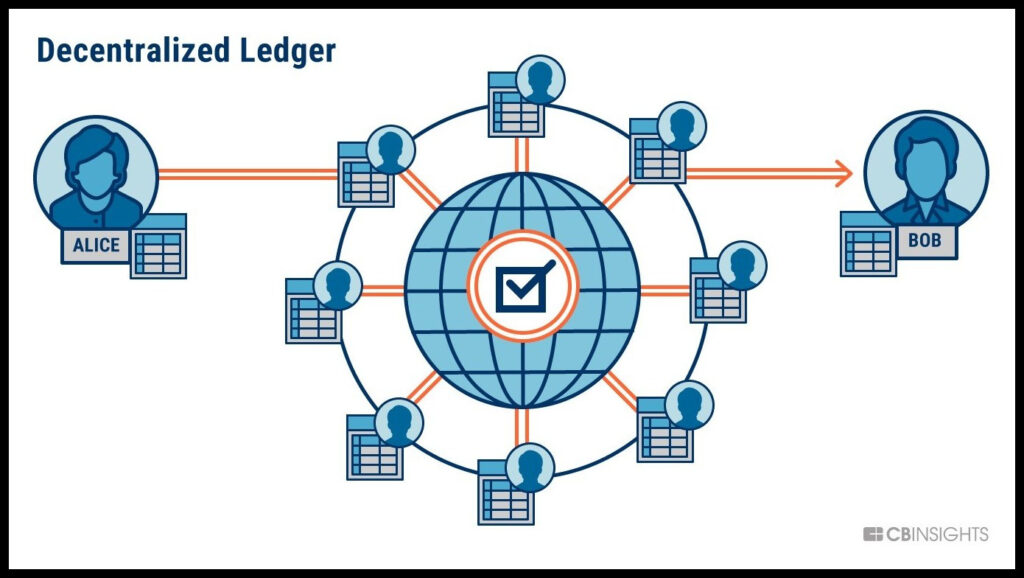
Blockchain is the newly emerging digital technology that establishes a decentralized infrastructure where data is stored using cryptography on a public ledger, giving ownership of data and identity to owners.
The biggest challenge in today’s world is cybersecurity. As new developments in the IT sector take place, a huge concern over cybercrimes has risen ever since the age of the internet.
Web3 emerges as the solution to cybercrimes. It is mainly built upon blockchain with peer-to-peer networks that process interactions across the world, which is why it is considered a highly secure technology.
This article introduces you to what is blockchain security and why it is so important in today’s digitalized world.
What is Blockchain Security?
Before we begin exploring this question, let’s get to know the basics. Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) in which different blocks store data; once a block reaches its capacity limit, a new block is created, leading to a chain of data blocks.
The information stored on this technology is democratized, which means it is shared with a network of processors. It is designed with a very trustworthy structure so that all members aka nodes have an equal distribution of assets.
Blockchain security is a risk management infrastructure shared by a network of professionals that prevents cyber threats, reduces risks of fraud, and has a proper regulatory framework to keep the transactions or processes running. It’s a highly secure system; perfect for storing confidential information.
Types of blockchain security
To understand this concept, you should know the types of blockchains that currently exist in the space.
- Private blockchain
- Public blockchain
- Permissioned blockchain
- Permissionless blockchain
Private blockchain
The Private blockchain is a closed network where information is shared with only a certain network of computers while one party has control over deciding who can be a member of this blockchain. Usually, business corporations utilize this type.
Public blockchain
This type allows anyone to join and approve transactions. The users stay anonymous with a public key to identify themselves, and the data is shared with the network to validate the operations on the protocol. Bitcoin Mining is the best example of this type of blockchain.
Permissioned blockchain
In this type, the users can only join the network to access transactions once they have permission from the controlling entity. They are given certificates to identify themselves on the platform.
Permissionless blockchain
Just as the name suggests, this blockchain doesn’t require any permission to join as a validator of transactions.
Why is blockchain security important?
Blockchain security ensures that the transactions or processes taking place on platforms are seamless and safe.
The ownership of data is a concern all over the world because, in Web2, the tech giants have control over identities and they can access them without the need for the owners’ consent. Web3 gives individuals the facility to own their data and share wherever and how much they want to with companies and firms.
Additionally, it also prevents your data from being leaked to scammers who might use social engineering to steal assets. All in all, blockchain security protects users’ data from being accessed by an unauthorized party.
Blockchain security issues and challenges
Needless to its highly-secure infrastructure, there are still some issues and challenges that Web3 developers and builders are yet to solve. Many risks exist on blockchain that users can only avoid if they are aware of and educated about them.
Some of the hardships and security concerns are
- Stolen Keys
- Social engineering
- Phishing attack
- Sybil attacks
- 51% Mining attack
- Computer hacks
- Routing attacks
1. Stolen Keys
The Stolen Key to access a wallet is a common crime in Web3 space. Since the only way to access a non-custodial wallet is to have the private phrase key, many attackers target people’s computers or databases to steal the keys and then access their digital assets.
Although this type of wallet ensures you have full ownership over your assets with no third-party involvement, if the keys get stolen, then your assets are nowhere safe.
2. Social Engineering
Just like in Web2, social engineering is common for blockchain users. The con artists can easily fool innocent victims into sharing their private keys or sensitive information to access platforms or steal assets.
Just recently, a scammer faked his position in a company to target Bored Ape owners for over a month and stole 14 NFTs worth $1 million.
3. Phishing attacks
If you’re not familiar with wallets, for any website to connect and access your assets, you need to sign approval. Well, hackers have cracked the code into creating fake links for phishing attacks through emails or social media.
Basically, an attacker fakes his identity or hacks into a major account and posts a fake link, which people sign in with their wallets. As a result, the attackers drain out all digital assets, causing huge losses to owners.
This is quite similar to the phishing phone calls that try to access bank accounts by faking their identity.
4. Sybil attack
Sybil attack is named after a book but it’s quite common in the IT world in which the hacker creates many fake identities to clog the network preventing it to work properly due to frequent login attempts altogether at one time.
When the network is unable to operate, the criminals take advantage of the vulnerability to drain information or assets.
5. 51% Mining attack
This attack takes place in blockchains with a proof-of-work mechanism where miners validate transactions and add them to the block using cryptography. If a group of attackers gains 50% dominance in the mining power, then they can control the network.
This is usually common in massive blockchains such as Bitcoin while private blockchains are most likely not vulnerable to this kind of attack.
6. Computer hacks
Computer hacks mean hackers cease a user’s operating system to access and steal their private information. The attackers can access any blockchain network from the computer if they have been granted access.
7. Routing attacks
Routers are also vulnerable to attack. Blockchain makes transactions in huge data forms through the internet. Once the router is in the hands of a cybercriminal, they can easily access information through the internet service providers.
The biggest challenge with this kind of vulnerability is there’s no way for a user to know about a routing attack. Everything happens in the background which sometimes can cost the loss of confidential information or stored digital currencies.
Blockchain Security Solutions
To tackle the above-mentioned vulnerabilities, there are many solutions through the use of tools and testing phases that ensure every blockchain is secure for transactions. These tools are designed by expert developers to detect any loopholes that might be in danger of being attacked.
Before we jump into the tools, you should know the most common practices for blockchain solutions:
- The governance model should be secure for member organizations and individuals
- Data access should be handled by identity and access management (IAM)
- Safe storage of identity keys
- Follow the regulatory requirements stated by authorities
- Secure ledger entries through the privileged access management (PAM) solution
- Use API for safe transactions
- Frequent vulnerability assessment and penetration testing
- Recover all security loopholes
- Audit Certification from blockchain security firms
- Strong multi-factor authentication and cryptographic key management.
- A data classification system to protect users’ information
- Effective Recovery plan for disasters to compensate based on applications and participants.
- Strong logic to resolve block collisions
Blockchain holds great responsibility when it comes to security because many applications and participants lay their trust in it. Whether it’s a private or public network, it’s important to have a strong infrastructure that doesn’t quiver over minor attacks.
Examples
Following are examples of how different companies are adopting blockchain security on their platforms:
Coinbase
Coinbase is the world’s largest exchange, especially in the United States, that allows users to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies. This trading platform stores data about users and their wallets using encryption, which is entirely impossible to decrypt. Coinbase staff are also employed through a severe background check to ensure they have no contact with cybercriminals.
Ethereum
Every transaction goes through vigorous checking, done by a network of members in the community selected through staking native tokens, ETH. To explain it simply: Users are supposed to stake their coins to gain the power as a node to make decisions on the transaction through mutual agreement. These nodes also inspect every vulnerable or unusual behavior.
Ethereum is the second-largest blockchain in the world having the highest number of NFTs and dApps built on it. It’s the most reliable network that has maintained its security through a distributed trust model aka proof-of-stake.
Ledger
Ledger is a hardware wallet where users can store their virtual currencies. The private keys are kept in the form of USB devices, making them least vulnerable to internet attacks. Each device contains a Secure Element smart chip and BOLOS proprietary operating system to leverage blockchain security.
Blockchain Security jobs
Web3 has opened a new market for jobs, so people who think they don’t fit into the IT world can join the blockchain world and establish their careers here.
Blockchain security is all about understanding the security risks and having the ability to manage them effectively. A developer who has extensive knowledge and experience in this field is open to many high-paying jobs because there are very few people who sign up for them.
Compared to other technology-based industries, blockchain is new so there are a lot of open positions in blockchain security since scams and hacks are quite common in this industry.
Some of the positions include
- Penetration tester
- Engineering manager
- IT specialist
- Protocol security engineer
- Security risk analyst
- Security Architect
And many more.
Blockchain Security Salary
There’s no fixed range in terms of salary because it depends on what company you’re joining but based on our estimates, an employee in Blockchain security is most likely to make around $85k to $130k per year while some sources also show crypto security experts can earn $400K per year due to massive demand in the market.
Final words
Blockchain security requires a team of experts and professionals who work together to come up with a highly effective model that can tackle all governance, business, technology, and transaction risks.
In order to keep networks running, this sector is continuously doing research and analysis for better controls and measures to keep users and decentralized applications safe.