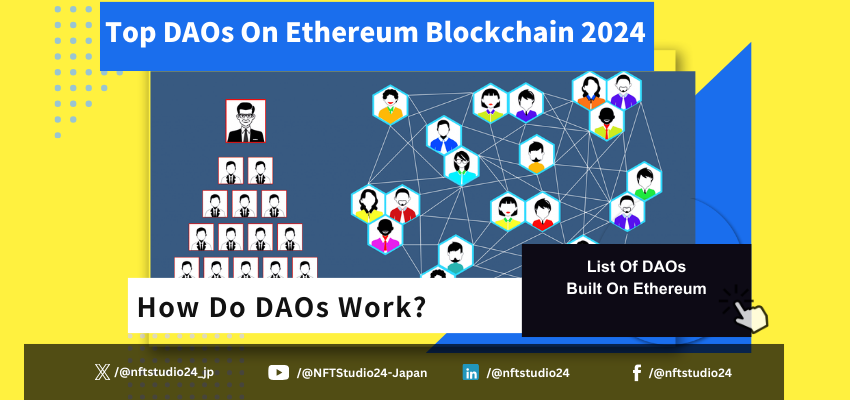
Featured Interview
Featured Interview
Bitcoin, Ethereum & Crypto News
Cryptocurrency Price Prediction
Expert's Voice

Read More
Been reading about biotech and considering to use crypto to accelerate research funding in biotech.

Read More
Consumer utility in web3 is happening - you can feel it.

Read More
As Bitcoin nears its all-time high, investor sentiment is mixed, with some taking profits while many hold on.

Read More
I wish there was modular, open source software that could be used to coordinate resources, align incentives, and enable real time settlement

Read More
Wins and losses will come. If I survive, I can leap forward with the next victory.

Read More
If history repeats Next Bull Market peak may occur Sept-Oct 2025.

Read More
Self-custody is important. And social recovery and multisig is a great way to do it.

Read More
Bitcoin’s market cap is higher right now than it has ever been in history.
Read More
Every year in crypto is like 10, makes sense.
Read More
You earn $ by utilising the business opportunities you come across.
Previous
Next
- Advertisement -